Supply Chain Threat: The attack by Chinese spies reached almost 30 U.S. companies, including Amazon and Apple, by compromising America’s technology supply chain, according to extensive interviews with government and corporate sources in this article.
(Bloomberg) In 2015, Amazon.com Inc. began quietly evaluating a startup called Elemental Technologies, a potential acquisition to help with a major expansion of its streaming video service, known today as Amazon Prime Video. Based in Portland, Ore., Elemental made software for compressing massive video files and formatting them for different devices.
Its technology had helped stream the Olympic Games online, communicate with the International Space Station, and funnel drone footage to the Central Intelligence Agency. Elemental’s national security contracts weren’t the main reason for the proposed acquisition, but they fit nicely with Amazon’s government businesses, such as the highly secure cloud that Amazon Web Services (AWS) was building for the CIA.
To help with due diligence, AWS, which was overseeing the prospective acquisition, hired a third-party company to scrutinize Elemental’s security, according to one person familiar with the process. The first pass uncovered troubling issues, prompting AWS to take a closer look at Elemental’s main product: the expensive servers that customers installed in their networks to handle the video compression.
These servers were assembled for Elemental by Super Micro Computer Inc., a San Jose-based company (commonly known as Supermicro) that’s also one of the world’s biggest suppliers of server motherboards, the fiberglass-mounted clusters of chips and capacitors that act as the neurons of data centers large and small. In late spring of 2015, Elemental’s staff boxed up several servers and sent them to Ontario, Canada, for the third-party security company to test, the person says.
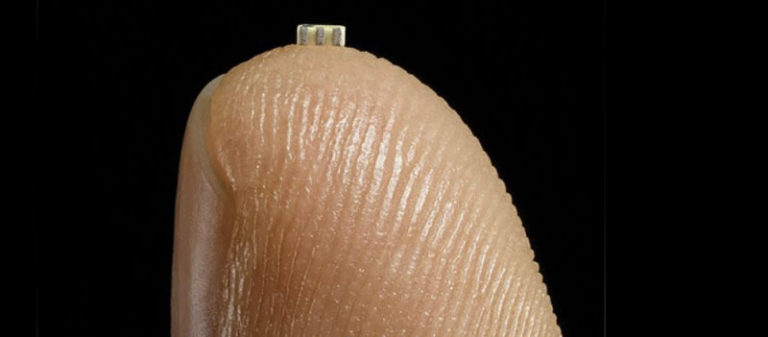
Nested on the servers’ motherboards, the testers found a tiny microchip, not much bigger than a grain of rice, that wasn’t part of the boards’ original design.
Amazon reported the discovery to U.S. authorities, sending a shudder through the intelligence community. Elemental’s servers could be found in Department of Defense data centers, the CIA’s drone operations, and the onboard networks of Navy warships. And Elemental was just one of hundreds of Supermicro customers.
During the ensuing top-secret probe, which remains open more than three years later, investigators determined that the chips allowed the attackers to create a stealth doorway into any network that included the altered machines. Multiple people familiar with the matter say investigators found that the chips had been inserted at factories run by manufacturing subcontractors in China.
This attack was something graver than the software-based incidents the world has grown accustomed to seeing. Hardware hacks are more difficult to pull off and potentially more devastating, promising the kind of long-term, stealth access that spy agencies are willing to invest millions of dollars and many years to get.
There are two ways for spies to alter the guts of computer equipment. One, known as interdiction, consists of manipulating devices as they’re in transit from manufacturer to customer. This approach is favored by U.S. spy agencies, according to documents leaked by former National Security Agency contractor Edward Snowden. The other method involves seeding changes from the very beginning.
One country in particular has an advantage executing this kind of attack: China, which by some estimates makes 75 percent of the world’s mobile phones and 90 percent of its PCs. . . .
. . . . In Supermicro, China’s spies appear to have found a perfect conduit for what U.S. officials now describe as the most significant supply chain attack known to have been carried out against American companies.
One official says investigators found that it eventually affected almost 30 companies, including a major bank, government contractors, and the world’s most valuable company, Apple Inc. . . .
. . . . Elemental also started working with American spy agencies. In 2009 the company announced a development partnership with In-Q-Tel Inc., the CIA’s investment arm, a deal that paved the way for Elemental servers to be used in national security missions across the U.S. government.
Public documents, including the company’s own promotional materials, show that the servers have been used inside Department of Defense data centers to process drone and surveillance-camera footage, on Navy warships to transmit feeds of airborne missions, and inside government buildings to enable secure videoconferencing.
NASA, both houses of Congress, and the Department of Homeland Security have also been customers. This portfolio made Elemental a target for foreign adversaries. . . . .
. . . Today, Supermicro sells more server motherboards than almost anyone else. It also dominates the $1 billion market for boards used in special-purpose computers, from MRI machines to weapons systems. Its motherboards can be found in made-to-order server setups at banks, hedge funds, cloud computing providers, and web-hosting services, among other places. Supermicro has assembly facilities in California, the Netherlands, and Taiwan, but its motherboards—its core product—are nearly all manufactured by contractors in China.
The company’s pitch to customers hinges on unmatched customization, made possible by hundreds of full-time engineers and a catalog encompassing more than 600 designs. The majority of its workforce in San Jose is Taiwanese or Chinese, and Mandarin is the preferred language, with hanzi filling the whiteboards, according to six former employees. Chinese pastries are delivered every week, and many routine calls are done twice, once for English-only workers and again in Mandarin. . . .
. . . . With more than 900 customers in 100 countries by 2015, Supermicro offered inroads to a bountiful collection of sensitive targets. “Think of Supermicro as the Microsoft of the hardware world,” says a former U.S. intelligence official who’s studied Supermicro and its business model. “Attacking Supermicro motherboards is like attacking Windows. It’s like attacking the whole world.”. . . . (read the whole article!)




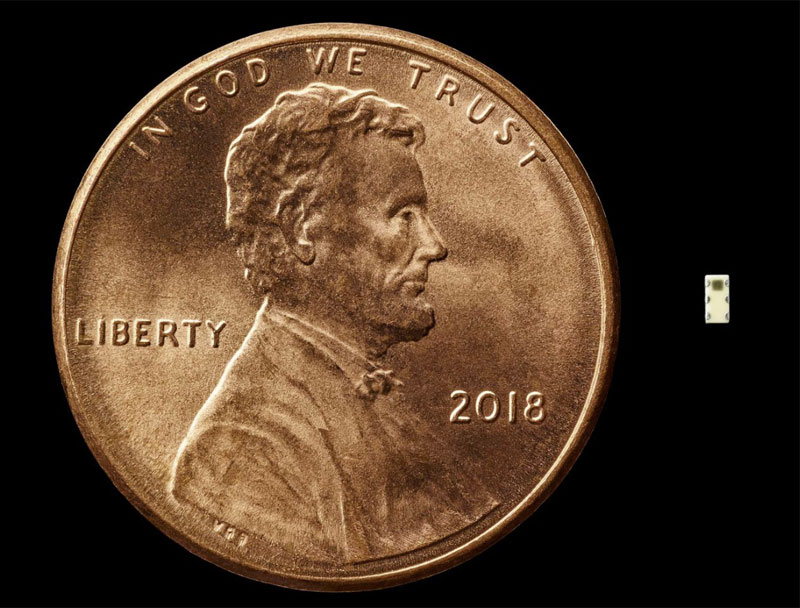







You must be logged in to post a comment.